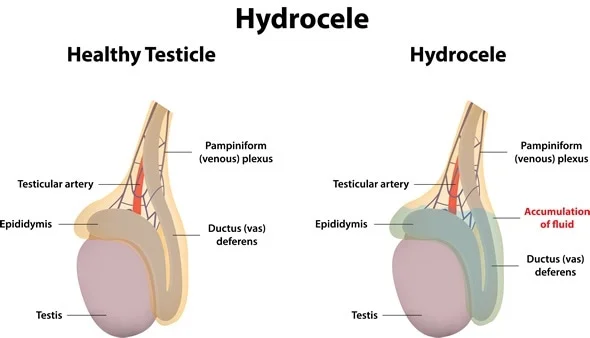
A hydrocele a blown type single lap complicated in the scrotum that occurs when liquid is collected in the thin sheath surrounding one of the testes. Hydrocele is common in newborns and usually disappears without treatment until the age of 1 year.
Hydrocele is usually not painful or harmful and may not need any treatment. But if you have scrotal swelling, consult your doctor to rule out other causes.

Why hydrocele :
A hydrocele can develop before birth. Normally, the testicles descend from the abdominal cavity of the developing child into the scrotum. A bag accompanies each testicle, allowing the fluid to surround the testicles. Usually, each bag closes and the liquid is absorbed.
Sometimes the liquid remains after closing the bag (non-communicating hydrocele). The fluid is usually gradually absorbed in the first year of life. But occasionally, the sac remains open. The sac may change size or if the scrotal sac is compressed, fluid may flow back into the abdomen. Communicating hydroceles are often associated with inguinal hernia.
A hydrocele can develop as a result of injury or inflammation in the scrotum. Inflammation could be caused by an infection in the testicle or in the small tubes wrapped behind each testicle (epididymitis).
Natural remedy to heal testicular hydrocele with plants
The use of herbal products to treat testicular hydrocele usually gives excellent results and allows you to avoid surgery. In general, except for late diagnosis, our natural treatment makes it easy to treat hydrocele. It therefore leaves no after-effects. This natural remedy is a secret of nature for those who wish to cure testicular hydrocele without surgery. Thus, the solution is often found in nature!

The natural remedy to cure testicular hydrocele permanently that we offer you is composed of two elements: a herbal tea and an ointment. The combined action of the powder and ointment is very effective. It leads to the effective absorption of all the liquid contained in the scrotum. Thus, the first effects will be felt very quickly.
To contact our experts please call or write to us on the following number, tel / WhatsApp : 00229 99 546 463
Natural remedies for hydrocele
Celery juice perfectly removes fluid from the body

Celery is a vegetable crop - a storehouse of vitamins and minerals, which are important in the postoperative period for home monitoring of hydrocele. The daily rate of juice consumption, which can be broken down over time into smaller portions. - at least 0.5 cups.
To give the drug a more pleasant taste, a pure mass of celery in the form of porridge can be diluted with cabbage, carrot, or beet juice.
Parsley to cure hydrocele
- It helps normalize blood flow, which is the main condition for preventing and eliminating stagnant processes;
- Regulates the outflow of fluid from the scrotum, thereby eliminating hydrocele;
- Parsley contributes to the improvement of potency, and a full-fledged intimate life is necessary for a man, so that his genitals can be released from the secretions that are secreted, due to which hydrocele can appear, which may require intervention surgical.

Prepare the medicine in this way.
-
We wash the parsley at 800 g, put it in a saucepan, pour the milk at 1 l.
-
We send the mixture from which we will prepare the drug for swelling of the testicles in men, to the oven, where it should simply remain (the mixture should not boil) for about 4 hours.
-
In the production of milk, the means will be two times less than the original volume, and the thinning of the composition must be completed.
-
We wipe the mixture from the oven, cool and then decant.
Why does fluid collect in the scrotum
In an adult man and a newborn or boy under one year of age, the causes of dropsy differ. What factors influence the onset of the disease:
-
While still in utero, the genitals begin to form in the male embryo, but they are found in the abdominal cavity. Before birth, the testes descend into the scrotum through the abdominal process. If it does not tighten in time, the fluid passes through this passage to the testicles, and a newborn is diagnosed with congenital dropsy. Until they reach a year of age, doctors watch for changes in the scrotum. At this point, in most cases, the boy's edema goes away on its own.
-
An adult man notices swelling, the appearance of dropsy in the inguinal area after suffering bacterial genital infections, trauma to external male organs and surgeries for inguinal hernia . The reason for this is a violation of the outflow of lymph from the space of the testis.
Also read : Homemade tips to recognize a testicular hydrocele
Diagnosis of a hydrocele
To diagnose a hydrocele, your doctor will perform a physical exam. If you have a hydrocele, your scrotum will be swollen, but you will not have any pain. Your doctor will not be able to feel your testicle well through the bag full of fluids.
Your doctor may check the sensitivity of the scrotum by the transillumination method. It allows your doctor to determine if there is fluid in the scrotum. If fluid is present, the scrotum will allow light to pass through and the scrotum will appear to light up as the light passes through. However, if the scrotal swelling is due to a solid mass (cancer), then the light will not shine through the scrotum. This test does not provide a definite diagnosis, but it can be very useful.
Your doctor may also apply pressure to your abdomen to check for another condition called an inguinal hernia;
Also read : Cure hydrocele in infants: natural remedy and treatment
Type of Hydrocele
The hydrocele can be:
Congenital hydrocele - is an accumulation of fluid around the testicle (testicular hydrocele) or in the spermatic cord (funicular hydrocele / spermatic cord cyst). It can occur in 1-2% of newborns;
Acquired hydrocele - fluid collection is caused by the imbalance between secretion and absorption of fluid from the vaginal serosa;
The mechanism of occurrence of the hydrocele is simple to understand. During intrauterine life the testicles form in the abdominal cavity, then migrate to the scrotum, "pushing" the peritoneum in the form of the peritoneo-vaginal canal to the scrotum.
After the testicle reaches the scrotum, this canal closes. In the case of boys with congenital hydrocele, this closure is not complete, leaving a narrow communication with the peritoneal cavity. This penetrates the peritoneal fluid, but cannot penetrate an intestinal loop, so the hydrocele cannot be complicated by a loop strangulation.
Congenital hydrocele can be:
Communicating - the entire peritoneo-vaginal canal persists and the fluid circulates between the scrotum and the peritoneal cavity. In this case there are variations in the volume of the scrotum, there are times when it seems that the hydrocele has disappeared. It is more voluminous in the evening and lower in the morning (after a period of decreased abdominal pressure during sleep);
Noncommunicating - the peritoneo-vaginal canal closed, but in the testicular vagina it remained liquid;
Sperm cord cyst - the peritoneal fluid persists along the peritoneo-vaginal canal, this canal closing inferior and superior to this cyst.