Fatty hepatosis or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD, steatosis) is a disease characterized by an excessive accumulation of fat (mainly triglycerides) in the liver. Normally, a certain amount of fat is present in the liver, but under the influence of certain pathological factors, the balance between fat synthesis and use can be disturbed. We will see how milk thistle fights against liver disease.

Plants to treat fatty liver disease
Do you suffer from fatty liver disease? If so, contact us and start an all-natural, effective treatment without side effects. This treatment will give you satisfaction after two months.
We are available on +229 99546463 by WhatsApp and direct call.
Grandmother's remedy for fatty liver disease: milk thistle tea
Thistle tea is an excellent home remedy for liver fat as this herb contains astringent properties, aiding digestion and stimulating appetite, which relieves symptoms of fatty liver disease such as loss of appetite, nausea. and vomiting.

Ingredients
- 2 teaspoons of thistle seeds
- 2 cups of water
Preparation mode
- Bring the water to a boil and after boiling add the thistle seeds.
- Let stand 15 minutes, filter and drink 30 minutes before meals.
This home remedy for liver fat should only complement the treatment for liver fat which should be done with diet, exercise, no smoking, and no alcoholic beverages.
Causes of fatty liver disease
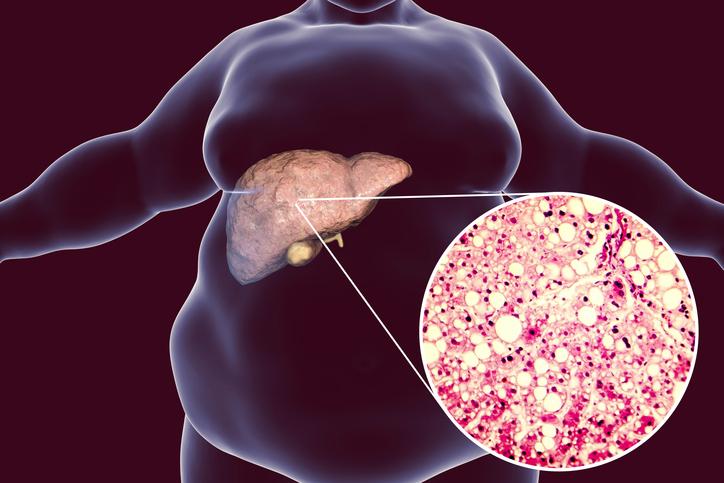
Hepatosis of the fatty liver is a very modern disease, because its causes are often:
- alcohol abuse (including the so-called alcoholism from beer);
- unhealthy diet (especially such a popular fast food);
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics and antidepressants.
Of course, hepatosis can develop against the background of serious diseases of the immune and endocrine systems, diabetes mellitus, obesity, but alcohol remains the most common cause.
Symptoms of fatty liver disease
With fatty liver hepatosis, an excess of fat produced by the body settles in the hepatocytes (organ cells), the cells are reborn, fibrosis can gradually begin and, as a result, cirrhosis of the liver. At the same time, the initial stage of the disease is almost asymptomatic, sometimes there are general signs of liver diseases: yellowing of the sclera and skin, often insignificant, pain and a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, vision cloudiness, nausea.
In addition to medication, fatty hepatosis can be treated with folk remedies. The fact is that in the early stages of the disease, although it has not yet started, the main role is played not by drugs, but by a correctly selected diet, which is quite compatible with the taking decoctions, herbal teas, fruit juices, etc.
What is elastometry or liver elastography?
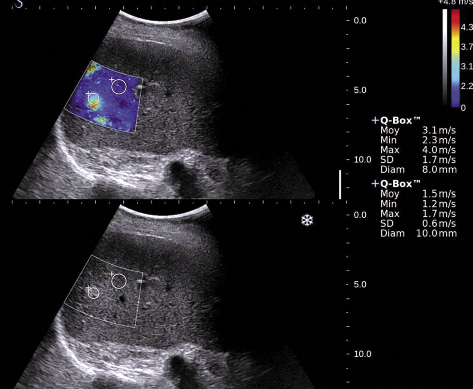
Elastometry (elastoraphy) or as it is also called fibroscanning of the liver is a modern, non-invasive method, without surgery, to diagnose the degree of fibrosis and the degree of fatty hepatosis, hepatic steatosis. Unlike biopsy, elastometry (elastography) of the liver allows the study of the entire organ, rather than a single fragment, which ensures high reliability of the results of the elastometric examination.
Why is hepatic elastometry necessary?
Examination of the liver on the Fibroscan machine can reliably determine the degree of liver damage, namely the degree of fibrosis and the degree of fatty hepatosis, without surgical intervention. The data obtained on the condition of the patient's liver allows the hepatologist to make an accurate diagnosis and choose the right treatment tactics, or correct previously prescribed treatment, if necessary. The sooner an accurate diagnosis is made and the right treatment started, the better the chances of maintaining a healthy liver.
How to prepare for liver elastometry
No special preparation is required for the examination with the Fibroscan device (elastometry / elastography). For ultrasound of the liver, it is recommended to undergo an examination on an empty stomach. You can drink water. The hunger interval should be at least 4 hours.
Who needs elastometry (elastography) - examination on the Fibroscan machine
- Elastometry as a preventive examination can be recommended for anyone over 40 years of age.
- A mandatory Fibroscan examination to assess the degree of liver damage should be performed for any liver disease:
- Viral hepatitis B, C, D.
- Fatty hepatosis - non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Alcoholic liver disease - alcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Autoimmune liver disease (autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis and others).
- Gilbert's syndrome and other hereditary liver diseases.
- If the risk of liver damage is high, elastometry (elastography) should be performed in patients:
- with diabetes mellitus,
- with high levels of cholesterol or triglycerides,
- with excess of the norm of indicators of cytolysis (ALT, AST, GGT), in case of violation of the clinical analysis of blood (decrease in the level of leukocytes and platelets),
- if you are overweight,
- with a frequent increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood.
- if cirrhosis is suspected or if cirrhosis is established.
Liver elastometry can detect early conditions in people who drink alcohol and take drugs that are toxic to the liver.
L'évaluation de l'état selon les données de l'élastométrie hépatique doit être effectuée avant le début du traitement et après le cours du traitement. Avec un degré élevé de lésions hépatiques (F3-F4), une diminution de la fibrose hépatique est observée pendant une longue période (plusieurs années), par conséquent, après un traitement, une surveillance constante est nécessaire.